Felite™ Resin Technology specializes in manufacturing and providing water softening resins for a range of applications such as industrial water softening, commercial softening, and residential softening, among others.
Home » Water Softener Resin Manufacturer
Home » Water Softener Resin Manufacturer
Water softener resins are commonly utilized to eliminate Calcium and Magnesium ions from water to protect pipelines in industrial settings or home appliances. With over 50 years of experience in producing water softener resins, Felite™ Resin Technology is a reliable supplier of this type of resin. Our gel and macroporous water softener resins are available in various specifications, including purity level (industrial grade & potable water grade), particle size (standard mesh, fine mesh, coarse mesh), and cross-linkage (4-16%).
Felite™ water softener resins are WQA certified and compatible with all commercially available brands of water softening equipment.


Felite™ Resin Technology specializes in manufacturing and providing water softening resins for a range of applications such as industrial water softening, commercial softening, and residential softening, among others.

Water softening is the process of removing calcium and magnesium ions from water. Ion exchange is the simplest and most cost-effective method for accomplishing this task.
Resins play an essential role in the water softening process. The performance of a water softener is largely determined by the quality of the resin used. Understanding how resins function can assist in selecting the ideal water softener and re-bedding an existing softener to meet the desired hardness and iron removal targets.
Water can dissolve massive amounts of substances. Therefore, we can say water is a universal solvent. While these substances dissolve in water, they can be ionic or non-ionic. Ionic particles either carry positive charges or negative charges. Non-ionic particles have no charge, and they are neutral.
Water that carries Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions more than the highest desirable level is called “Hard Water” or hardness in water. Elevated calcium and magnesium ions make it challenging to dissolve soaps in water and clog pipelines, reducing the efficiency of kettles and heaters.
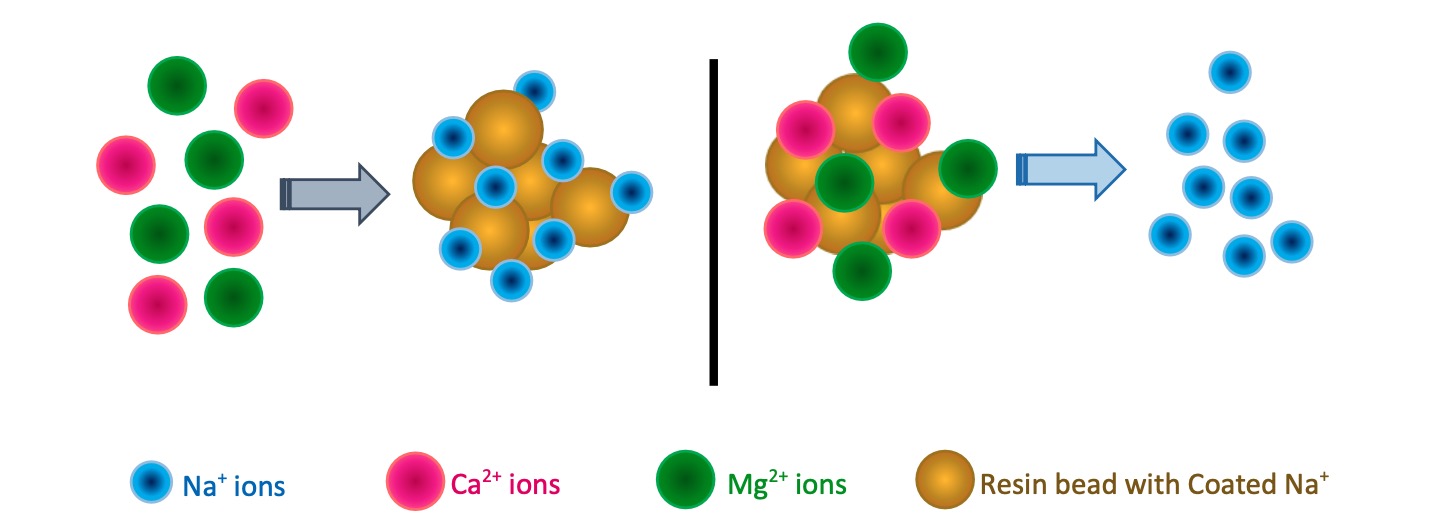
Water softening is the process that exchanges above cations inside the softener unit with the help of water softener resins.
Resins within the softening plant tightly hold its negatively charged anions which is attractive for any cations. At the initial stage, resin beads are coated with Na+ ions. During the process, Resins exchange Na+ ions with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. So softened water carries Na+ ions.
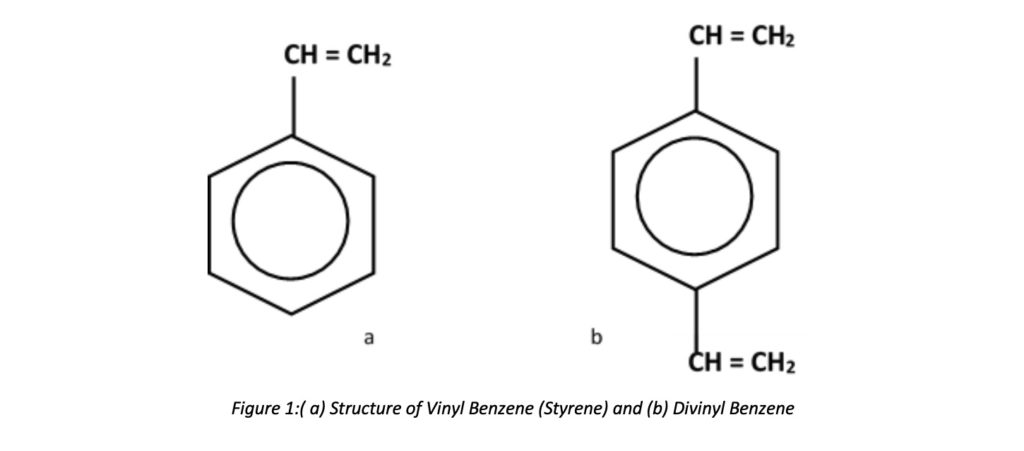
The most common materials of structure of water softener resins are Styrene and Divinyl Benzene(DVB). The DVB is the binding agent, and it holds the resin together. DVB amount used while manufacturing can define as cross-linking percentages. It simply describes that the resin bead strength depends on DVB.
Styrene and DVB are monomers in liquid form. But they are not dissolvable in water. While agitating, the monomers and water create small tiny monomer droplets suspended in the water phase. These small liquid droplets become hard plastic spheres (beads or copolymers) with proper agitation of the mixture and raising temperature. The beads are washed, dried, and screened.
After that, beads are functionalized (electrostatically charged) into an ion exchange resin. Kinetic performance of resins, resistance to oxidation, and service life of beads are mainly affected by the level of DVB. For example, approximately 2- 20% DVB content can be varied while manufacturing strong acid cation (SAC) exchange.structure
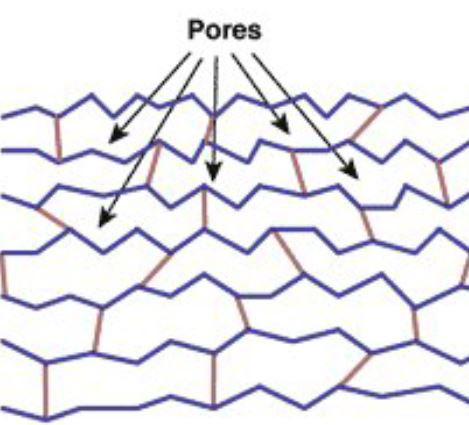
Gel resins generally have smaller pores (approx. 1 to 2 nm, hydrated) in the resin structure, higher initial exchange capacity, and exchange rate.
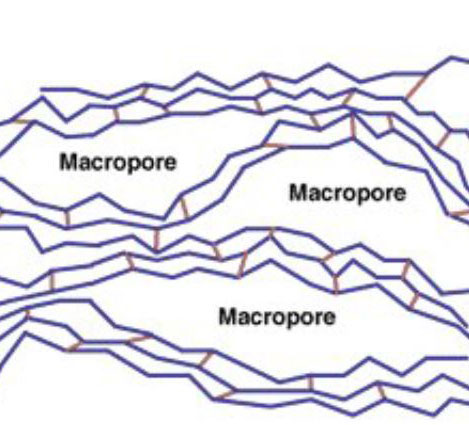
Macroporous resins are usually considered to elute foulants more effectively due to the larger pore structure (approx. 20 to 100 nm, hydrated). They can often stand up better in harsher operating environments, such as high temperatures and higher chlorine feed water. Macroporous resin has a slow exchange rate than gel resin.
Resin manufacturers produce resins into the standard grading from 0.3-1.2 mm. sometimes, special grades are made; fine mesh 0.2-0.5mm, coarse mesh 0.5-1.2mm are manufactured for different purposes.
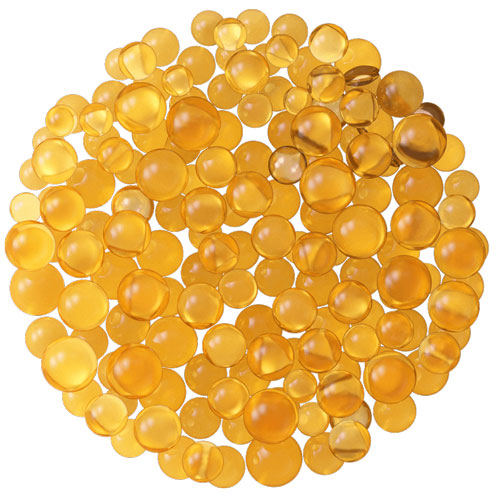



Fine mesh resins that increase the surface area for ion exchange can be used for softening due to their high operating capacities and ease of regeneration. Tiny resin beads are packed tightly in the vessel, which causes the water flow rate to slow. It is not suited for high flow systems and water with high turbidity.
Coarse mesh resins are specially manufactured for industrial high-flow water softening systems. They can minimize the pressure losses with suspended particles in raw water.
IX change does not occur on the surface but inside the copolymers. Plastic beads hold Na+ ions initially. When hard water runs through the resin bed, beads catch the divalent ions and release their monovalent ions (Na+ or K+). Negatively charged functional groups, which are immobile, hold these replacing cations at the interior of the resin bead, but rarely does it exchange ions at the bead’s surface.
When the resin bed gets saturated, hardness ions haven’t more space to create affinity with immobilized negative ions in resins. So we need to refresh resin; hence, the reverse ion exchange process should have proceeded. It is called “Regeneration.”
Use saline solution or brine solution (NaCl) to regenerate resin media. This solution should have enough strength to drive the reverse reaction of IX. Concentrated NaCl enters the resin bed and exchanges Na+ ions with hardness ions. The softener bed is getting reactive now. Before injection of brine solution, it is needed to be backwash the softener unit.
During the service cycle, the ionic contaminants are absorbed by the resins, producing the water’s qualities desired. This cycle continues until the resins in the column are exhausted, and regeneration process is required to restore the resins’ effectiveness.
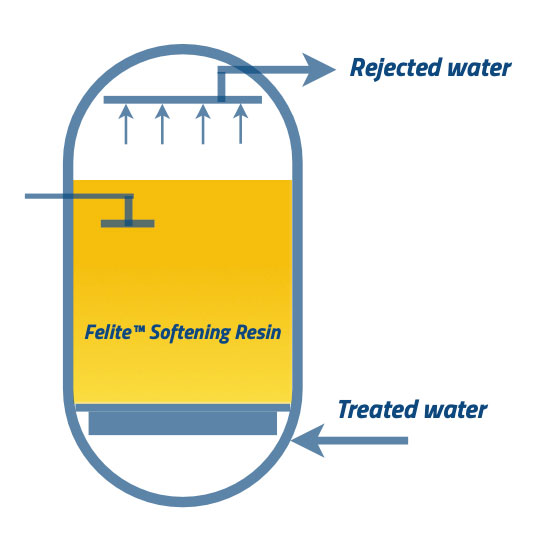
Backwash process is performed in CFR* only, and involves rinsing the resin to remove suspended solids and redistribute compacted resin beads. The agitation of the beads helps remove any fine particles and deposits from the resin surface.
CFR*: Co-flow Regeneration
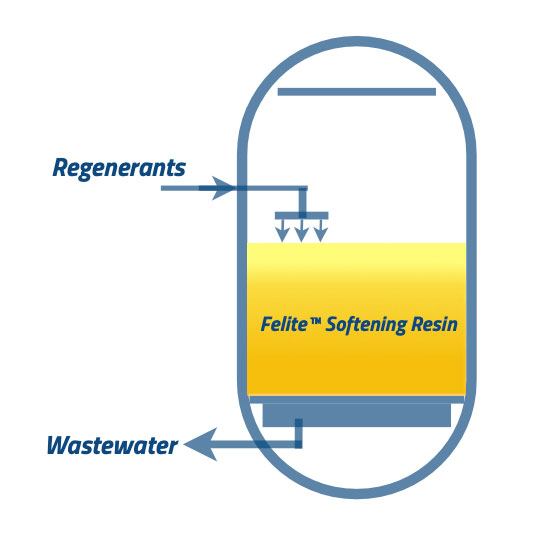
During the regeneration process, the regenerant solution is injected into the IX column at a low flow rate to allow adequate contact time with the resins. In the case of CFR* configuration, the regenerant is injected in the same direction of the service flow.
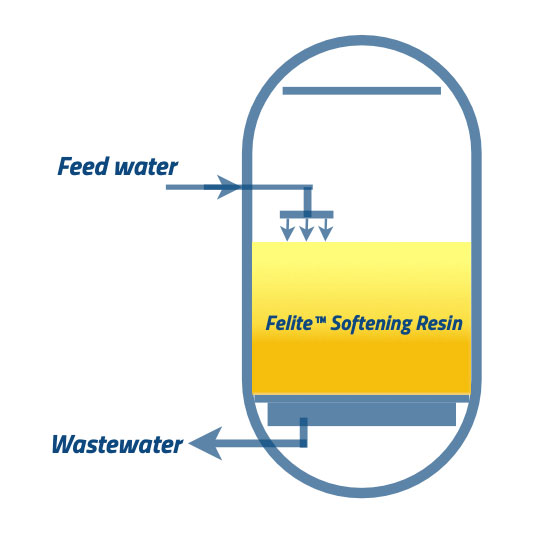
The regenerant is flushed out gradually by the slow flow of feed water, typically at the same flow rate as the regenerant solution. The flow rate of this “slow rinse” stage must be carefully managed to avoid damage to the resin beads.
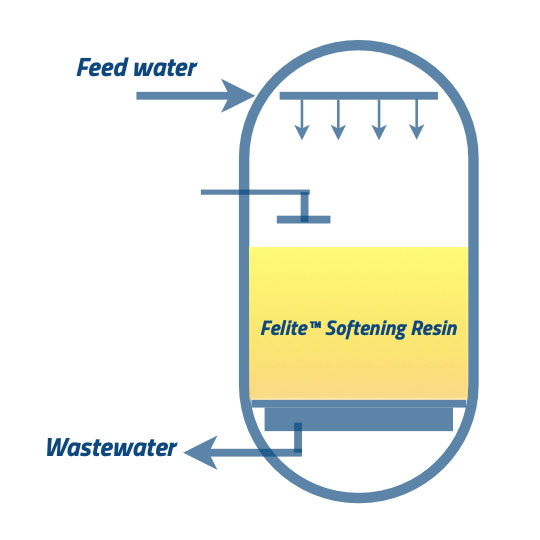
In the final step, the resins are rinsed with water at the same flow rate as the service process. The rinse cycle should continue until a target water quality level is reached before the service cycle commences again.
Now, your softening resin is ready to go.

Erica S.,
Water Treatment Specialist

David M.,
Production Manager
We use only top-quality materials and state-of-the-art facilities to ensure consistent performance and quality in our water softener resins.
“Removal process of Calcium and Magnesium ions from Water” called Water Softening. Ion exchanging is the simplest and most economically effective method for it.
Resins are essential materials throughout the whole process of water softening. Mainly, the performance of a water softener depends on the effectiveness of inserted resin. Knowing how resins work will help you select the best water softener and re-bedding your existing softener that meets your target; hardness and iron removal.
This article introduces information about water softening, including understanding its process, identifying various classifications of water softener resin, as well as comparing the pros and cons of different crosslinkage.
Water can dissolve massive amounts of substances. Therefore, we can say water is a universal solvent. While these substances dissolve in water, they can be ionic or non-ionic. Ionic particles either carry positive charges or negative charges. Non-ionic particles have no charge, and they are neutral.
Water that carries Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions more than the highest desirable level is called “Hard Water” or hardness in water. Elevated calcium and magnesium ions make it challenging to dissolve soaps in water and clog pipelines, reducing the efficiency of kettles and heaters.
Water softening is the process that exchanges above cations inside the softener unit with the help of water softener resins.
Resins within the softening plant tightly hold its negatively charged anions which is attractive for any cations. At the initial stage, resin beads are coated with Na+ ions. During the process, Resins exchange Na+ ions with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. So softened water carries Na+ ions.
The most common materials of construction of water softener resins are Styrene and Divinyl Benzene(DVB). The DVB is the binding agent, and it holds the resin together. DVB amount used while manufacturing can define as cross-linking percentages. It simply describes that the resin bead strength depends on DVB.
Styrene and DVB are monomers in liquid form. But they are not dissolvable in water. While agitating, the monomers and water create small tiny monomer droplets suspended in the water phase. These small liquid droplets become hard plastic spheres (beads or copolymers) with proper agitation of the mixture and raising temperature. The beads are washed, dried, and screened.
After that, beads are functionalized (electrostatically charged) into an ion exchange resin. Kinetic performance of resins, resistance to oxidation, and service life of beads are mainly affected by the level of DVB. For example, approximately 2- 20% DVB content can be varied while manufacturing strong acid cation (SAC) exchange.
Gel resins generally have smaller pores (approx. 1 to 2 nm, hydrated) in the resin structure, higher initial exchange capacity, and exchange rate.
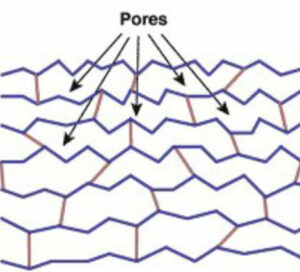
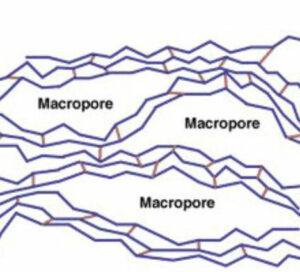
Macroporous resins are usually considered to elute foulants more effectively due to the larger pore structure (approx. 20 to 100 nm, hydrated). They can often stand up better in harsher operating environments, such as high temperatures and higher chlorine feed water. Macroporous resin has a slow exchange rate than gel resin.
IX change does not occur on the surface but inside the copolymers. Plastic beads hold Na+ ions initially. When hard water runs through the resin bed, beads catch the divalent ions and release their monovalent ions (Na+ or K+). Negatively charged functional groups, which are immobile, hold these replacing cations at the interior of the resin bead, but rarely does it exchange ions at the bead’s surface.
When the resin bed gets saturated, hardness ions haven’t more space to create affinity with immobilized negative ions in resins. So we need to refresh resin; hence, the reverse ion exchange process should have proceeded. It is called “Regeneration.”
Use saline solution or brine solution (NaCl) to regenerate resin media. This solution should have enough strength to drive the reverse reaction of IX. Concentrated NaCl enters the resin bed and exchanges Na+ ions with hardness ions. The softener bed is getting reactive now. Before injection of brine solution, it is needed to be backwash the softener unit.

It usually take 2 weeks for 1x20ft container quantity production;

Usually 1 week from our facility to Shanghai port by ground transportation;

This CIF price is quoted from China to the LA for your reference; 3 weeks on the way;
Want to get the accurate CIF price to your region? Or, request a sample?

Mix refined styrene and DVB liquid monomer, add initiator BPO and stir well; add dissolved inorganic dispersant and organic dispersant in the aqueous phase for high-temperature suspension polymerization into spherical particles; wash and cure to neutral by hot water at 95℃±2℃, dry and sieve to get white spherical beads.

The process is the reaction of styrene-DVB copolymer beads with 77.19% sulfuric acid to introduce sulfonic acid groups in the backbone. The water softener resin is obtained by gradient dilution of sulfuric acid with different specific gravity and water washing.

(1) Treat the industrial-grade softener resin with the organic solvent to remove residual monomer, then pretreat with refined hydrochloric acid and ionic membrane alkali to remove impurities dissolved in the acid and alkali;
(2) Steam 3 times with high-temperature and high-pressure steam in a hot water environment at 95℃~98℃ for 2 hours each time to remove the dissolved material in the resin;
(3) Use 8~10% refined hydrochloric acid, heat to 60℃±2℃, and the amount of regenerant is 8 times the volume of resin. Then after transforming to the sodium form, the potable water grade softener resin is obtained after washing with ultrapure water;


We’d love to answer any of your technical questions!

When using the ion-exchange process for industrial water softening, it is important to consider high water flow rates. In this application, resins with high capacity, strength, and regeneration ability are typically required.
Felite™ Resin Technology produces strong acid cation resins with fine & standard mesh that are designed to effectively perform water softening procedures.

Hard water can cause scaling, which can decrease the efficiency of household appliances, such as electrical equipment, sinks, and tubs. It can also lead to blockages in water supply drains and accumulation of soap scum.
To alleviate these issues, domestic water can be softened using a water softener that utilizes the ion exchange process.
With five decades of experience, Felite Resin Technology is well versed in this field. In other hand, you are dealing with the master. You can trust us with your needs and expectations.
In the past five decades, we’ve developed several softener resin models as per different customers and applications required, from standard mesh to fine mesh; from industrial grade to Non-solvent grade.

Want to know how we make doing business easier? Let’s talk.